NEWS | SOFTWARE | SHEET
Clear Cover for Slab, Beam, Column, Staircase, and Footing: Uses in Construction
In the realm of construction, attention to detail is paramount to ensure the safety, durability, and longevity of structures. One often-overlooked aspect that plays a critical role in the structural integrity of buildings is the clear cover.
The clear cover refers to the distance between the outer surface of the concrete and the innermost layer of reinforcement within structural elements such as slabs, beams, columns, staircases, and footings.
In this comprehensive blog article, we will delve into the concept of clear cover, its importance, and its specific uses in construction.
What is a Clear Cover?
Clear cover, also known as concrete cover, is the protective layer of concrete that surrounds and encases the reinforcement bars (rebar) within structural elements. It acts as a shield, safeguarding the reinforcement from environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and corrosion. The clear cover is specified in terms of thickness and varies depending on the type of structural element and its intended use.
Importance of Clear Cover
The clear cover serves several crucial functions in construction:
1. Corrosion Protection
One of the primary purposes of clear cover is to protect the embedded rebar from corrosion. Excessive moisture and the presence of corrosive substances can lead to the deterioration of reinforcement, weakening the structural element. Adequate clear cover acts as a barrier, preventing these harmful agents from reaching the rebar.
2. Durability
Clear cover enhances the durability of concrete structures. It shields the reinforcement from external forces, reducing the risk of damage or cracking. This, in turn, ensures the longevity of the structure, reducing maintenance costs over its lifespan.
3. Fire Resistance
In the event of a fire, the clear cover provides an extra layer of insulation, helping to maintain the structural integrity of the building for a longer period. This is critical for ensuring the safety of occupants and first responders.
4. Load Distribution
Clear cover also plays a role in distributing loads evenly across the reinforcement and preventing concentrated stress points. This ensures that the structural element can carry its intended loads safely.
Specific Uses of Clear Cover in Construction
Clear cover requirements can vary depending on the type of structural element. Let's explore its specific uses in different components of construction:
1. Clear Cover for Slabs
Slabs are horizontal structural elements that bear loads such as floor or roof loads. The clear cover for slabs is essential for protecting the reinforcement bars and preventing moisture penetration from above (e.g., rainwater) or below (e.g., rising damp from the ground).
2. Clear Cover for Beams
Beams are horizontal or sloping structural elements that transfer loads from the slabs or columns to the foundations. Adequate clear cover in beams ensures the protection of rebar and prevents premature failure due to corrosion or cracking.
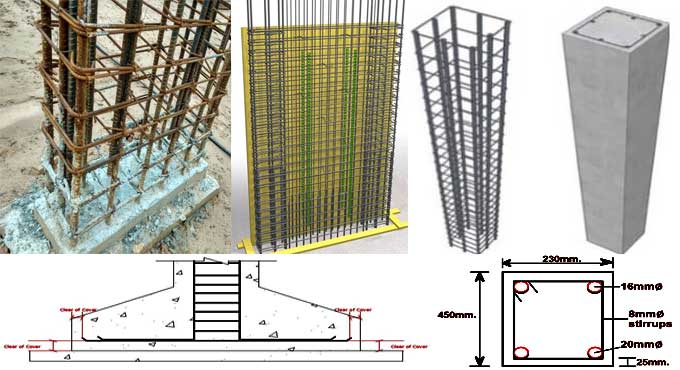
3. Clear Cover for Columns
Columns are vertical load-bearing elements that support the weight of the entire structure. The clear cover for columns is crucial to prevent corrosion of the vertical rebar, which can lead to structural instability.
4. Clear Cover for Staircases
Staircases are an integral part of many buildings. Clear cover in staircase construction ensures the safety and longevity of these elements, especially in outdoor or exposed environments.
5. Clear Cover for Footings
Footings, also known as foundations, are responsible for transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Adequate clear cover in footings prevents moisture and soil contaminants from compromising the integrity of the reinforcement.
Determining Clear Cover Thickness
The appropriate thickness of clear cover varies based on several factors:
1. Environmental Conditions
Clear cover requirements are influenced by the exposure conditions. For example, structures located in coastal areas or regions with high humidity levels may require thicker clear cover to protect against saltwater or moisture.
2. Structural Element Type
Different structural elements have varying clear cover thicknesses. Beams and columns typically have thicker clear covers compared to slabs.
3. Concrete Grade
The quality of the concrete mix also affects clear cover requirements. Higher-strength concrete may allow for thinner clear covers while maintaining the same level of protection.
4. Design Codes and Standards
Construction projects must adhere to local building codes and industry standards that specify clear cover requirements. Engineers and architects consider these regulations when designing structures.
5. Specific Project Requirements
Unique project requirements, such as seismic considerations or architectural specifications, can influence clear cover thickness.
Maintaining Clear Cover during Construction
Maintaining the specified clear cover during construction is critical to the overall success of a project. Several precautions can help ensure the protection of reinforcement:
1. Proper Formwork Installation
Careful installation of formwork, the temporary moulds used to shape concrete, is essential to ensure that the required clear cover is maintained during pouring and curing.
To get more details, go through the following video tutorial.
Lecturer: Civil Engineer
2. Quality Control
Implementing quality control measures throughout the construction process, including concrete placement and compaction, helps prevent errors that could compromise the clear cover.
3. Adequate Concrete Protection
After the structure is completed, protective measures such as waterproofing and coatings can be applied to further safeguard the concrete and maintain the clear cover's integrity.
Clear cover may seem like a minor detail in construction, but its significance cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in protecting the reinforcement, ensuring structural durability, and enhancing the overall safety and performance of buildings. From slabs and beams to columns, staircases, and footings, clear cover requirements vary depending on the structural element's function and environmental conditions.
In a world where construction practices continue to evolve, the understanding and implementation of clear cover standards remain a fundamental aspect of responsible construction. Engineers, architects, and construction professionals must prioritize clear cover specifications to create buildings that stand the test of time, providing safety and reliability for generations to come.