NEWS | SOFTWARE | SHEET
Building Foundations: The Uses and Differences of Stone Masonry and Brick Masonry
What do you mean by Masonry Work?
Masonry work involves the construction of structures using materials like bricks, stones, or blocks. It requires skilled craftsmanship and involves arranging, bonding, and joining these materials to create walls, foundations, floors, and other architectural elements.
Masons use tools and mortar to lay the materials in a specific pattern, ensuring strength, stability, and aesthetic appeal. Masonry work is essential in various types of construction, providing durability, fire resistance, and weather resistance.
What is Brick Masonry in Construction?
Brick masonry, the art of constructing structures using bricks, has been practiced for centuries and continues to be widely used in the field of construction. Here are some of the common uses of brick masonry:
1. Load-bearing walls: One of the primary uses of brick masonry is in constructing load-bearing walls. These walls support the weight of the entire structure and provide stability and strength. Brick masonry walls are durable and can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for both residential and commercial buildings.
2. Facades and cladding: Bricks are often used as an outer layer or cladding material for buildings to enhance their aesthetic appeal. Brick facades provide a classic, timeless look and can be customized with various patterns, colours, and textures. They also offer protection against weather elements and improve insulation.
3. Retaining walls: Brick masonry is frequently used in the construction of retaining walls. These walls are built to resist the lateral pressure of soil and retain it at different levels. Brick retaining walls are known for their strength and stability, making them ideal for supporting terraces, gardens, or other landscape features.
4. Fireplaces and chimneys: The heat resistance and durability of bricks make them a popular choice for constructing fireplaces and chimneys. Brick masonry can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for containing and channelling heat and smoke safely.
5. Paving and flooring: Bricks can be used for paving walkways, driveways, patios, and other outdoor spaces. Brick pavers are durable, slip-resistant, and easy to maintain. In addition to outdoor applications, bricks are sometimes used for interior flooring to create a rustic or traditional look.
6. Arches and decorative elements: The versatility of bricks allows for the construction of various architectural features, such as arches, columns, and decorative elements. These elements add visual interest and character to buildings, whether they are used for structural support or purely aesthetic purposes.
7. Landscaping and garden structures: Bricks are often employed in landscaping projects to build structures like garden walls, raised beds, and seating areas. Brick masonry blends well with natural surroundings and can help create a cohesive design in outdoor spaces.
It is worth noting that brick masonry is just one of the many construction techniques available, and its use depends on factors such as local availability, building codes, architectural design, and project requirements.
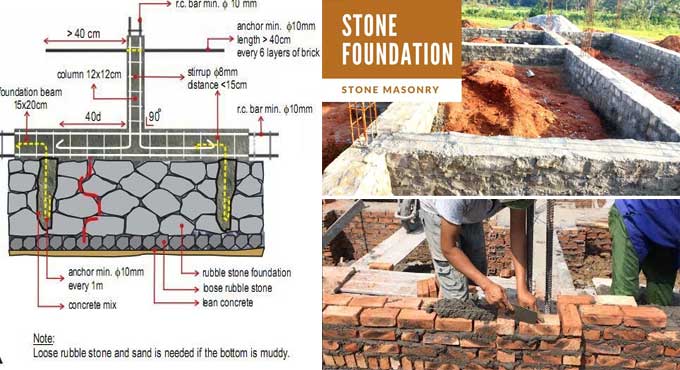
What is Stone Masonry in Construction?
Stone masonry is a construction method that involves using stones as the primary building material. It encompasses the use of both irregularly shaped stones (rubble masonry) and precisely cut and dressed stones to create walls, structures, and architectural features.
Stone masonry is employed in various construction applications, including:
1. Building construction: Stone masonry is used to create load-bearing walls, foundations, and structural elements in both residential and commercial buildings.
2. Historical preservation: Stone masonry is crucial for restoring and preserving historical buildings, monuments, and cultural heritage sites.
3. Landscaping and hardscaping: Stones are used to build retaining walls, garden walls, terraces, pathways, and other landscaping features in outdoor spaces.
4. Bridges and infrastructure: Stone masonry is utilized in the construction of bridge abutments, piers, and other infrastructure elements where strength and durability are paramount.
5. Facades and cladding: Stones are used as cladding material to enhance the appearance and aesthetics of buildings.
6. Interior design: Stone masonry can be incorporated into interior design elements such as fireplaces, accent walls, and flooring for their visual appeal and durability.
The use of stone masonry provides durability, aesthetic appeal, and a connection to natural materials. However, it is important to note that stone masonry requires skilled labour and careful craftsmanship to ensure proper construction and longevity.
How Can You Differentiate Between Brick Masonry and Stone Masonry?
Brick masonry and stone masonry are two distinct construction techniques that use different materials and have some key differences. Here are the main contrasts between brick masonry and stone masonry:
1. Materials: The primary difference lies in the materials used. Brick masonry involves using bricks, which are rectangular-shaped blocks made from clay or concrete. Stone masonry, on the other hand, uses natural stones, which can be irregularly shaped or precisely cut and dressed.
2. Shape and Size: Bricks have a standardized rectangular shape and uniform size, allowing for consistent and precise construction. In contrast, stones used in stone masonry can vary significantly in shape, size, and texture, offering a more organic and varied appearance.
3. Construction Technique: Brick masonry is typically built using mortar, which is a mixture of cement, sand, and water. Bricks are laid in courses with mortar joints, creating a uniform and consistent structure. Stone masonry can be constructed using mortar or dry stone techniques, where stones are stacked without mortar, relying on their interlocking properties.
4. Aesthetic Appeal: Brick masonry often has a uniform and clean appearance due to the regular shape and size of bricks. It can be customized with various colours and textures, but generally provides a more structured and consistent look. Stone masonry offers a more natural and varied aesthetic, showcasing the unique texture, colour, and shape of the stones used.
5. Strength and Durability: Both brick masonry and stone masonry can provide strength and durability. However, stone masonry, particularly when using large, precisely cut stones, can have higher compressive strength and structural stability compared to brick masonry.
6. Availability and Cost: Bricks are mass-produced and readily available, making them more affordable and accessible than natural stones. Natural stones used in stone masonry can vary in availability and cost, depending on the type, source, and processing required.
To get more details, go through the following video tutorial.
Lecturer: Civil Engineers
7. Skill and Expertise: While both techniques require skill and expertise, stone masonry often demands more craftsmanship due to the irregular shape and size of stones. Proper stone selection, cutting, dressing, and placement require specialized knowledge and experience.
The choice between brick masonry and stone masonry depends on factors such as architectural design, desired aesthetic, availability of materials, project requirements, and budget considerations. Both techniques have their advantages and can create durable and visually appealing structures.